Acetic Acid Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: acetic acid
- Brand Name: Acetic Acid
side effects drug center acetic acid (acetic acid) drug
Drug Description
What is Acetic Acid and how is it used?
Acetic Acid is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of bacterial or fungal infections in the ear. Acetic Acid may be used alone or with other medications.
Acetic Acid belongs to a class of drugs called Otics, Other; Anti-infectives, Otic.
It is not known if Acetic Acid is safe and effective in children younger than 3 years of age.
What are the possible side effects of Acetic Acid?
Acetic Acid may cause serious side effects including:
- hives,
- difficulty breathing,
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, and
- severe burning or irritation after using the ear drops
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Acetic Acid include:
- mild stinging or burning with the first use
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Acetic Acid. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
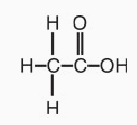
Acetic Acid Otic Solution, USP is a solution of acetic acid (2%), in a propylene glycol vehicle containing propylene glycol diacetate (3%), benzethonium chloride (0.02%), sodium acetate (0.015%), and citric acid. The empirical formula for acetic acid is CH3COOH, with a molecular weight of 60.05. The structural formula is:
 |
Acetic Acid Otic Solution is available as a nonaqueous otic solution buffered at pH 3 for use in the external ear canal.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
For the treatment of superficial infections of the external auditory canal caused by organisms susceptible to the action of the antimicrobial.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Carefully remove all cerumen and debris to allow Acetic Acid Otic Solution to contact infected surfaces directly. To promote continuous contact, insert a wick of cotton saturated with Acetic Acid Otic Solution into the ear canal; the wick may also be saturated after insertion. Instruct the patient to keep the wick in for at least 24 hours and to keep it moist by adding 3 to 5 drops of Acetic Acid Otic Solution every 4 to 6 hours. The wick may be removed after 24 hours but the patient should continue to instill 5 drops of Acetic Acid Otic Solution 3 or 4 times daily thereafter, for as long as indicated. In pediatric patients, 3 to 4 drops may be sufficient due to the smaller capacity of the ear canal.
HOW SUPPLIED
Acetic Acid Otic Solution, USP, containing 2% acetic acid, is available in 15 mL and 30 mL measured-drop, safety-tip plastic bottles.
Storage
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed.
Manufactured by: VINTAGE PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC, Huntsville, AL 35811. 8180671 R3/05. FDA Rev date: 2/24/2005
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Stinging or burning may be noted occasionally; local irritation has occurred very rarely.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No information provided.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Discontinue promptly if sensitization or irritation occurs.
PRECAUTIONS
Transient stinging or burning may be noted occasionally when the solution is first instilled into the acutely inflamed ear.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 3 years have not been established.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No information provided.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to Acetic Acid Otic Solution or any of the ingredients. Perforated tympanic membrane is considered a contraindication to the use of any medication in the external ear canal.
Clinical Pharmacology
Acetic acid is antibacterial and antifungal; propylene glycol is hydrophilic and provides a low surface tension; benzethonium chloride is a surface active agent that promotes contact of the solution with tissues.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
No information provided. Please refer to the WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS sections.
