Vision Loss Symptoms
Loss of vision can occur suddenly or develop gradually over time. Vision loss may be complete (involving both eyes) or partial, involving only one eye or even certain parts of the visual field. Vision loss is different from blindness that was present at birth, and this article is concerned with causes of vision loss in an individual who previously had normal vision. Vision loss can also be considered as loss of sight that cannot be corrected to a normal level with eyeglasses. The causes of loss of vision are extremely varied and range from conditions affecting the eyes to conditions affecting the visual processing centers in the brain. Impaired vision becomes more common with age. Common causes of vision loss in the elderly include diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, and cataracts.
Other causes of vision loss
- Bacterial Infection
- CMV Retinitis
- Corneal Scars
- Eye Tumor
- Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Medications
- Onchocerciasis
- Stargardt's Disease
- Toxins/Poisoning
- Trauma
- Viral Infections of the Eye
- Vitamin A Deficiency
Causes of Vision Loss
-

Amblyopia
Amblyopia, or "lazy eye," is a childhood condition where one eye has poorer vision than the other. Amblyopia occurs when one eye has much better focus than the other eye. The condition is diagnosed by having an eye exam. Amblyopia may be treated with an eye patch, eye drops containing atropine, or surgery. Most cases of amblyopia resolve with early detection and treatment.
-

Birthmark
A birthmark is any abnormal mark, spot, or bump that is present in or around the time of birth on the skin of an infant. Types of birthmarks include cafe au lait marks, Mongolian spots, strawberry marks, and others. Depending on the birthmark type, birthmarks can be removed by scalpel surgery, lasers, and rarely radiation.
-

Blindness
Blindness is the state of being sightless. Causes of blindness include macular degeneration, stroke, cataract, glaucoma, infection and trauma. Symptoms and signs may include eye pain, eye discharge, or the cornea or pupil turning white. Treatment of blindness depends upon the cause of the blindness.
-
Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
A brain tumor can be either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant), primary, or secondary. Common symptoms of a primary brain tumor are headaches, seizures, memory problems, personality changes, and nausea and vomiting. Causes and risk factors include age, gender, family history, and exposure to chemicals. Treatment is depends upon the tumor type, grade, and location.
-
Cataracts
A cataract is an eye disease that causes the eye's lens to become cloudy and opaque with decreased vision. Causes of cataracts include diabetes, hypothyroidism, certain genetic illnesses, hyperparathyroidism, atopic dermatitis, and certain medications. Cataract symptoms and signs include a decrease in vision and a whitish color to the affected eye. Treatment for cataracts may involve cataract surgery.
-

Coats Disease
Coats disease is a rare eye condition that typically progresses to vision loss or blindness in one eye. Gradual vision loss is usually the first symptom, followed by a cloudy white or yellow pupil due to the presence of a cataract. Treatment focuses on limiting the blood vessel progression and may involve cryotherapy or laser photocoagulation. Read about symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is a rare, degenerative, invariably fatal brain disorder. CJD generally appears in the later years and runs a rapid course. Symptoms of CJD include failing memory, lack of coordination, visual disturbances, failing memory, blindness, weakness, and eventually coma. There are three major categories of CJD; 1) sporadic CJD, 2) hereditary CJD, and 3) acquired CJD. There is no cure for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
-
Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The two types of diabetes are referred to as type 1 (insulin dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin dependent). Symptoms of diabetes include increased urine output, thirst, hunger, and fatigue. Treatment of diabetes depends on the type.
-

Does NMO Cause Fatigue?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) or Devic disease is a rare, autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) doesn't cause fatigue, but living with the disease can lead to fatigue.
-

Does NMO Show on MRI?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) or Devic disease is a rare, autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the choice of diagnostic method for neuromyelitis optica (NMO).
-

Does Retinoblastoma Cause Blindness?
Retinoblastoma is a cancer of the eye that begins in the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive lining inside the eye. Retinoblastoma most commonly affects young children and rarely occurs in adults. Retinoblastoma can affect vision and even lead to blindness.
-
Eye Problems and Diabetes
Diabetes and eye problems are generally caused by high blood sugar levels over an extended period of time. Types of eye problems in a person with diabetes include glaucoma, cataracts, and retinopathy. Examples of symptoms include blurred vision, headaches, eye aches, pain, halos around lights, loss of vision, watering eyes. Treatment for eye problems in people with diabetes depend on the type of eye problem. Prevention of eye problems include reducing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, and maintaining proper blood glucose levels.
-
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a common eye condition in which the fluid pressure inside the eye rises because of slowed fluid drainage from the eye. If untreated, glaucoma may damage the optic nerve and other parts of the eye, causing the loss of vision or even blindness.
-

Is MS Contagious? (Multiple Sclerosis)
Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a degenerative disease of the covering around the nerves in the central nervous system (CNS). Researchers and doctors don't know the exact cause, but many theorize that it may be due to environmental triggers, an autoimmune disease, and viruses (infections). Symptoms of MS include vision changes, paralysis, vertigo, heat intolerance, slurred speech, sexual dysfunction, and urinary incontinence (the inability to urinate). There's no vaccine or cure for MS, but the progression and symptoms of the disease can be treated.
-

Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) annually affects one child in every thousand. There are six types of JRA. Treatment of juvenile arthritis depends upon the type the child has and should focus on treating the symptoms that manifest.
-

Leprosy
Leprosy (Hansen's disease) is a disfiguring disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium leprae bacteria. The disease is spread from person to person through nasal secretions or droplets. Symptoms and signs of leprosy include numbness, loss of temperature sensation, painless ulcers, eye damage, loss of digits, and facial disfigurement. Leprosy is treated with antibiotics and the dosage and length of time of administration depends upon which form of leprosy the patient has.
-

Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Low blood pressure, also referred to as hypotension, is blood pressure that is so low that it causes symptoms or signs due to the low flow of blood through the arteries and veins. Some of the symptoms of low blood pressure include light-headedness, dizziness, and fainting if not enough blood is getting to the brain. Diseases and medications can also cause low blood pressure. When the flow of blood is too low to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to vital organs such as the brain, heart, and kidneys; the organs do not function normally and may be permanently damaged.
-
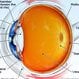
Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a disease that gradually destroys the central vision. In people over 60, AMD is a leading cause of vision loss. Wet AMD occurs when abnormal blood vessels behind the retina start to grow under the macula, leaking blood and fluid and causing rapid vision loss. In dry AMD, light-sensitive cells slowly break down in the macula, resulting in gradual vision loss. Pain is not associated with either form of AMD.
-

Migraine Headache
Migraine headache is a type of headache associated with a sensitivity to light, smells, or sounds, eye pain, severe pounding on one side of the head, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. The exact cause of migraine headaches is not known. Triggers for migraine headaches include certain foods, stress, hormonal changes, strong stimuli (loud noises), and oversleeping. Treatment guidelines for migraines include medicine, pain management, diet changes, avoiding foods that trigger migraines, staying hydrated, getting adequate sleep, and exercising regularly. Prevention of migraine triggers include getting regular exercise, drinking water daily, reducing stress, and avoiding trigger foods.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis or MS is an autoimmune disorder in which brain and spinal cord nerve cells become demyelinated. This damage results in symptoms that may include numbness, weakness, vertigo, paralysis, and involuntary muscle contractions. Different forms of MS can follow variable courses from relatively benign to life-threatening. MS is treated with disease-modifying therapies. Some MS symptoms can be treated with medications.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Symptoms and Treatments
Multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms vary from person to person, and can last for days to months without periods of remission. Symptoms of MS include sexual problems and problems with the bowel, bladder, eyes, muscles, speech, swallowing, brain, and nervous system. The early symptoms and signs of multiple sclerosis usually start between age 20 and 40. MS in children, teens, and those over age 40 is rare. Treatment options for multiple sclerosis vary depending on the type and severity of symptoms. Medications may be prescribed to manage MS symptoms.
-

Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, or river blindness, is a parasitic disease that may cause blindness. It is transmitted by the bite of a female blackfly. Symptoms include skin depigmentation, vision loss, and itch. Ivermectin is used to treat the disease.
-
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve, the structure that connects the eye to the brain. The precise cause of optic neuritis is unknown, but it is thought to be a type of autoimmune disorder. Optic neuritis most commonly develops due to an autoimmune disorder that may be triggered by a viral infection.
-
Paget's Disease
Paget's disease, also called Paget's disease of bone, is a chronic bone disorder due to irregular breakdown and formation of bone tissue. Paget's disease symptoms include bone pain, headaches and hearing loss, pressure on nerves, increased head size, hip pain, and damage to cartilage of joints.
-

Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a disorder of the muscles and joints that causes pain and stiffness in the arms, neck, shoulders, and buttocks. Treatment for polymyalgia rheumatica aims to reduce inflammation with aspirin, ibuprofen, and low doses of cortisone medications.
-

Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
Pseudotumor Cerebri (intracranial hypertension) is a condition where there is an increase in pressure of fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid or CSF) mimicing a brain tumor. The cause is unknown. The most common symptom is headache but also include eye-pain, vision loss and double vision. Pseudotumor cerebri is diagnosed with MRI or CAT scans and treated by discontinuing offending medications (if applicable), weight loss and diuretic medications. The condition can also be helped by repeated drainage of spinal fluid using the lumbar puncture.
-
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is the separation of the retina from its attachments to the underlying eye tissue. Symptoms of retinal detachment include flashing lights and floaters. Highly nearsighted young adults and those who've had cataract surgery are at higher risk for retinal detachment.
-

Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic condition that causes retinal degeneration and eventual vision loss. Symptoms include night blindness and tunnel vision. Visual field testing and electrophysiological testing are essential in diagnosing RP. Though there is no cure for RP, vitamin A therapy and an omega-3-rich diet may be recommended for patients to slow disease progression.
-

Strabismus (Crossed Eyes)
Strabismus, or crossed eyes, is a condition in which the eyes do not align in the usual way. The condition may be congenital or the result of a problem with the control of the muscles of the eyes. Strabismus may cause double vision, headaches, eyestrain, and problems with depth perception and peripheral vision. Treatment may involve physical therapy, vision therapy, surgery, or wearing glasses.
-
Stroke
A stroke is an interruption of the blood supply to part of the brain caused by either a blood clot (ischemic) or bleeding (hemorrhagic). Symptoms of a stroke may include weakness, numbness, double vision or vision loss, confusion, vertigo, difficulty speaking or understanding speech. A physical exam, imaging tests, neurological exam, and blood tests may be used to diagnose a stroke. Treatment may include administration of clot-busting drugs, supportive care, and in some instances, neurosurgery. The risk of stroke can be reduced by controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and stopping smoking.
-
Trachoma
Trachoma is an infectious disease caused by the Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria. Symptoms and signs include redness and irritation of the eyes with tearing. Trachoma is diagnosed by examining the eyes and eyelids. Treatment involves a single dose of azithromycin (Zithromax) or the use of topical tetracycline (Achromycin) ointment. Infected individuals should be counseled about sanitation and taught simple cleanliness.
-

Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA, Mini-Stroke)
When a portion of the brain loses blood supply, through a blood clot or embolus, a transient ischemic attack (TIA, mini-stroke) may occur. If the symptoms do not resolve, a stroke most likely has occurred. Symptoms of TIA include: confusion, weakness, lethargy, and loss of function to one side of the body. Risk factors for TIA include vascular disease, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Treatment depends upon the severity of the TIA, and whether it resolves.
-
Treacher Collins Syndrome
Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS) is a rare genetic condition that affects the development of the bones and tissues of the face. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and include: Malformations of the eyes Anomalies of the structures of the external and middle ear Feeding or swallowing difficulties. Treatment of symptoms requires a multidisciplinary approach. Sometimes surgery may help relieve a patient's symptoms.
-
Usher Syndrome
There are three types of Usher (Usher's) syndrome, the most common condition that affects both vision and hearing. The major symptoms of Usher syndrome include retinitis pigmentosa (night-blindness and a loss of peripheral vision), and hearing loss. Usher syndrome is a genetic condition. There is no cure for Usher syndrome.
-
Uveitis
Uveitis is inflammation of the eye. Symptoms include blurred vision, eye pain, eye redness, photophobia, and floaters. Treatment may involve prescription eyedrops, antibiotics, and wearing dark glasses.
-
What Is the Best Treatment for Macular Edema?
Macular edema is a type of swelling inside the retina of the eye. The best approach to treatment requires addressing the underlying cause of macular edema, and it may include injections, steroids, eye drops, laser treatment and vitrectomy surgery.
- Amblyopia
- Birthmark
- Blindness
- Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
- Cataracts
- Coats Disease
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
- Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
- Does NMO Cause Fatigue?
- Does NMO Show on MRI?
- Does Retinoblastoma Cause Blindness?
- Eye Problems and Diabetes
- Glaucoma
- Is MS Contagious? (Multiple Sclerosis)
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
- Leprosy
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- Macular Degeneration
- Migraine Headache
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Symptoms and Treatments
- Onchocerciasis
- Optic Neuritis
- Paget's Disease
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica
- Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
- Retinal Detachment
- Retinitis Pigmentosa
- Strabismus (Crossed Eyes)
- Stroke
- Trachoma
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA, Mini-Stroke)
- Treacher Collins Syndrome
- Usher Syndrome
- Uveitis
- What Is the Best Treatment for Macular Edema?
