Polytrim Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim ophthalmic solution, usp, sterile
- Brand Name: Polytrim
side effects drug center polytrim (polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim ophthalmic solution, usp, sterile) drug
Drug Description
What is Polytrim and how is it used?
Polytrim is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Bacterial Conjunctivitis. Polytrim may be used alone or with other medications.
Polytrim belongs to a class of drugs called Antibiotics, Ophthalmic Combos.
It is not known if Polytrim is safe and effective in children younger than 2 months of age.
What are the possible side effects of Polytrim?
- increasing redness, burning, stinging or itching of the eye
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Polytrim include:
- eye irritation (redness, burning, stinging, or itching), and
- eyelid swelling,
- itching,
- increased redness,
- tearing of the eye, and
- rash
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Polytrim. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
POLYTRIM® (polymyxin B sulfate and trimethoprim ophthalmic solution, USP) is a sterile antimicrobial solution for topical ophthalmic use. It has pH of 4.0 to 6.2 and osmolality of 270 to 310 mOsm/kg.
Chemical Names
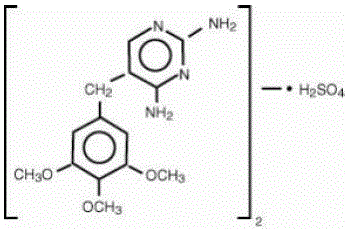
Trimethoprim sulfate, 2,4-Diamino-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl) pyrimidine sulfate, is a white, odorless, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 678.72 and the following structural formula:
 |
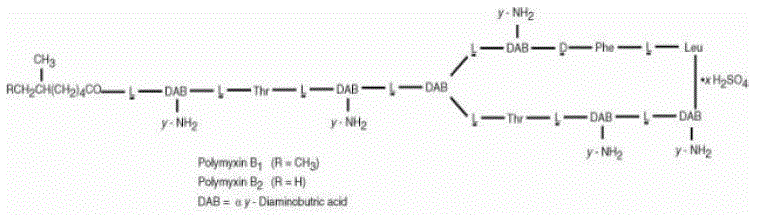
Polymyxin B sulfate is the sulfate salt of polymyxin B1 and B2 which are produced by the growth of Bacillus polymyxa (Prazmowski) Migula (Fam. Bacillaceae). It has a potency of not less than 6,000 polymyxin B units per mg, calculated on an anhydrous basis. The structural formulae are:
 |
Contains
Actives: polymyxin B sulfate 10,000 units/mL; trimethoprim sulfate equivalent to 1 mg/mL. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.04 mg/mL. Inactives: purified water; sodium chloride; and sulfuric acid. May also contain sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
POLYTRIM® Ophthalmic Solution is indicated in the treatment of surface ocular bacterial infections, including acute bacterial conjunctivitis, and blepharoconjunctivitis, caused by susceptible strains of the following microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus viridans, Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.*
*Efficacy for this organism in this organ system was studied in fewer than 10 infections.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
In mild to moderate infections, instill one drop in the affected eye(s) every three hours (maximum of 6 doses per day) for a period of 7 to 10 days.
HOW SUPPLIED
POLYTRIM® (polymyxin B sulfate and trimethoprim ophthalmic solution, USP) is supplied sterile in opaque white low density polyethylene ophthalmic dispenser bottles and tips with white high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
10 mL in 10 mL bottle - NDC 0023-7824-10
Storage
Store at 15° - 25° C (59° - 77° F) and protect from light.
Distributed by: Allergan USA, Inc. Madison, NJ 07940. Revised: July 2018
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The most frequent adverse reaction to POLYTRIM® Ophthalmic Solution is local irritation consisting of increased redness, burning, stinging, and/or itching. This may occur on instillation, within 48 hours, or at any time with extended use. There are also multiple reports of hypersensitivity reactions consisting of lid edema, itching, increased redness, tearing, and/or circumocular rash. Photosensitivity has been reported in patients taking oral trimethoprim.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information Provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
NOT FOR INJECTION INTO THE EYE. If a sensitivity reaction to POLYTRIM® occurs, discontinue use. POLYTRIM® Ophthalmic Solution is not indicated for the prophylaxis or treatment of ophthalmia neonatorum.
PRECAUTIONS
General
As with other antimicrobial preparations, prolonged use may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If superinfection occurs, appropriate therapy should be initiated.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted with polymyxin B sulfate or trimethoprim.
Mutagenesis
Trimethoprim was demonstrated to be non-mutagenic in the Ames assay. In studies at two laboratories no chromosomal damage was detected in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells at concentrations approximately 500 times human plasma levels after oral administration; at concentrations approximately 1,000 times human plasma levels after oral administration in these same cells, a low level of chromosomal damage was induced at one of the laboratories. Studies to evaluate mutagenic potential have not been conducted with polymyxin B sulfate.
Impairment Of Fertility
Polymyxin B sulfate has been reported to impair the motility of equine sperm, but its effects on male or female fertility are unknown.
No adverse effects on fertility or general reproductive performance were observed in rats given trimethoprim in oral dosages as high as 70 mg/kg/day for males and 14 mg/kg/day for females.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with polymyxin B sulfate. It is not known whether polymyxin B sulfate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity.
Trimethoprim has been shown to be teratogenic in the rat when given in oral doses 40 times the human dose. In some rabbit studies, the overall increase in fetal loss (dead and resorbed and malformed conceptuses) was associated with oral doses 6 times the human therapeutic dose.
While there are no large well-controlled studies on the use of trimethoprim in pregnant women, Brumfitt and Pursell, in a retrospective study, reported the outcome of 186 pregnancies during which the mother received either placebo or oral trimethoprim in combination with sulfamethoxazole. The incidence of congenital abnormalities was 4.5% (3 of 66) in those who received placebo and 3.3% (4 of 120) in those receiving trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. There were no abnormalities in the 10 children whose mothers received the drug during the first trimester. In a separate survey, Brumfitt and Pursell also found no congenital abnormalities in 35 children whose mothers had received oral trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole at the time of conception or shortly thereafter.
Because trimethoprim may interfere with folic acid metabolism, trimethoprim should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
The oral administration of trimethoprim to rats at a dose of 70 mg/kg/day commencing with the last third of gestation and continuing through parturition and lactation caused no deleterious effects on gestation or pup growth and survival.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when POLYTRIM® Ophthalmic Solution is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 2 months have not been established (see WARNINGS).
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No Information Provided
CONTRAINDICATIONS
POLYTRIM® Ophthalmic Solution is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its components.
Clinical Pharmacology
Trimethoprim is a synthetic antibacterial drug active against a wide variety of aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative ophthalmic pathogens. Trimethoprim blocks the production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. This binding is stronger for the bacterial enzyme than for the corresponding mammalian enzyme and therefore selectively interferes with bacterial biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins.
Polymyxin B, a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic, is bactericidal for a variety of gram-negative organisms, especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It increases the permeability of the bacterial cell membrane by interacting with the phospholipid components of the membrane.
Blood samples were obtained from 11 human volunteers at 20 minutes, 1 hour and 3 hours following instillation in the eye of 2 drops of ophthalmic solution containing 1 mg trimethoprim and 10,000 units polymyxin B per mL. Peak serum concentrations were approximately 0.03μg/mL trimethoprim and 1 unit/mL polymyxin B.
Microbiology
In vitro studies have demonstrated that the anti-infective components of POLYTRIM® are active against the following bacterial pathogens that are capable of causing external infections of the eye:
Trimethoprim
Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus aegyptius, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis (indole-negative), Proteus vulgaris (indolepositive), Enterobacter aerogenes and Serratia marcescens.
Polymyxin B
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes and Haemophilus influenzae.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the eye, fingers, or other source. This precaution is necessary if the sterility of the drops is to be maintained.
If redness, irritation, swelling or pain persists or increases, discontinue use immediately and contact your physician. Patients should be advised not to wear contact lenses if they have signs and symptoms of ocular bacterial infections.
