Ozobax
- Generic Name: baclofen oral solution
- Brand Name: Ozobax
side effects drug center ozobax (baclofen oral solution) drug
Drug Description
OZOBAX
(baclofen) Oral Solution
DESCRIPTION
OZOBAX (baclofen) oral solution is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA-ergic) agonist available as 5 mg/5 mL solution for oral administration. Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-butanoic acid, and its structural formula is:
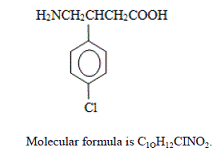 |
Molecular Weight is 213.66. Baclofen USP is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, and insoluble in chloroform. The OZOBAX (baclofen) oral solution inactive ingredients are: citric acid anhydrous, glycerin, natural grape flavor, methylparaben, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate dihydrate, and sucralose. May also contain sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
OZOBAX is indicated for the treatment of spasticity resulting from multiple sclerosis, particularly for the relief of flexor spasms and concomitant pain, clonus, and muscular rigidity.
OZOBAX may also be of some value in patients with spinal cord injuries and other spinal cord diseases.
Limitations Of Use
OZOBAX is not indicated in the treatment of skeletal muscle spasm resulting from rheumatic disorders.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
Initiate OZOBAX with a low dosage, preferably in divided doses, administered orally. The following gradually increasing dosage regimen is suggested, but should be adjusted based on clinical response and tolerability:
5 mL (5 mg) three times a day for three days
10 mL (10 mg) three times a day for three days
15 mL (15 mg) three times a day for three days
20 mL (20 mg) three times a day for three days
Additional increases may be necessary up to the maximum recommended dosage of 80 mg daily (20 mg four times a day).
Discontinuation Of OZOBAX
When discontinuing OZOBAX, reduce the dosage slowly and avoid abrupt withdrawn from the drug to help minimize the risk of adverse reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
Oral Solution: 5 mg/5 mL baclofen as a clear, colorless solution with a grape aroma
OZOBAX (baclofen) Oral Solution contains 5 mg/5 mL baclofen. It is a clear, colorless solution with a grape aroma and is supplied in bottles of 473 mL, NDC 69528-301-16.
Storage And Handling
Must be refrigerated. Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
Manufactured by: Entreprises Importfab, Inc. 50 Hymus Blvd. Pointe-Claire, QC, Canada H9R 1C9. Manufactured for: Metacel Pharmaceuticals, LLC Athens, GA 30601. Revised: Sep 2019
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Adverse Reactions from Abrupt Withdrawal of OZOBAX [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Neonatal Withdrawal Symptoms [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Drowsiness and Sedation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Poor Tolerability in Stroke Patients [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Exacerbation of Psychotic Disorders, Schizophrenia, or Confusional States [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Exacerbation of Autonomic Dysreflexia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Exacerbation of Epilepsy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Posture and Balance Effects [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Ovarian Cysts [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reaction is transient drowsiness. In one controlled study of 175 patients, transient drowsiness was observed in 63% of those receiving baclofen compared to 36% of those in the placebo group. Other common adverse reactions (up to 15%) are dizziness and weakness. Adverse reactions with a frequency of ≥1% are listed in Table 1.
Table 1:Common (≥1%) Adverse Reactions in
Patients Treated with Baclofen for Spasticity
| ADVERSE REACTION | PERCENT |
| Drowsiness | 10-63% |
| Dizziness | 5-15% |
| Weakness | 5-15% |
| Nausea | 4-12% |
| Confusion | 1-11% |
| Hypotension | 0-9% |
| Headache | 4-8% |
| Insomnia | 2-7% |
| Constipation | 2-6% |
| Urinary Frequency | 2-6% |
| Fatigue | 2-4% |
The following adverse reactions not included in Table 1, classified by body system, were also reported:
Neuropsychiatric: euphoria, excitement, depression, hallucinations, paresthesia, muscle pain, tinnitus, slurred speech, coordination disorder, tremor, rigidity, dystonia, ataxia, blurred vision, nystagmus, strabismus, miosis, mydriasis, diplopia, dysarthria, epileptic seizure
Cardiovascular: dyspnea, palpitation, chest pain, syncope
Gastrointestinal: dry mouth, anorexia, taste disorder, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and positive test for occult blood in stool
Genitourinary: enuresis, urinary retention, dysuria, impotence, inability to ejaculate, nocturia, hematuria
Other: rash, pruritus, ankle edema, excessive perspiration, weight gain, nasal congestion
The following laboratory tests have been found to be abnormal in patients receiving baclofen: increased SGOT, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and elevation of blood sugar.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
CNS Depressants And Alcohol
OZOBAX can cause CNS depression, including drowsiness and sedation, which may be additive when used concomitantly with other CNS depressants or alcohol [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Adverse Reactions From Abrupt Withdrawal Of OZOBAX
Abrupt discontinuation of baclofen, regardless of the cause, has resulted in adverse reactions that include hallucinations, seizures, high fever, altered mental status, exaggerated rebound spasticity, and muscle rigidity, that in rare cases has advanced to rhabdomyolysis, multiple organ-system failure, and death. Therefore, reduce the dosage slowly when OZOBAX is discontinued, unless the clinical situation justifies a rapid withdrawal.
Neonatal Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms in neonates whose mothers were treated with oral baclofen throughout pregnancy have been reported starting hours to days after delivery. The symptoms of withdrawal in these infants have included increased muscle tone, tremor, jitteriness, and seizure. If the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus and OZOBAX is continued during pregnancy, gradually reduce the dosage and discontinue OZOBAX before delivery. If slow withdrawal is not feasible, advise the parents or caregivers of the exposed neonate of the potential for neonatal withdrawal.
Drowsiness And Sedation
Drowsiness and sedation have been reported in up to 63% of patients taking baclofen, the active ingredient in OZOBAX [see ADVERSE REACTIONS]. Patients should avoid operation of automobiles or other dangerous machinery and activities made hazardous by decreased alertness when starting OZOBAX or increasing the dose until they know how the drug affects them. Advise patients that the central nervous system depressant effects of OZOBAX may be additive to those of alcohol and other CNS depressants.
Poor Tolerability In Stroke Patients
OZOBAX should be used with caution in patients who have had a stroke. Baclofen has not significantly benefited patients with stroke. These patients have also shown poor tolerability to the drug.
Exacerbation Of Psychotic Disorders, Schizophrenia, Or Confusional States
OZOBAX should be used with caution in patients suffering from psychotic disorders, schizophrenia, or confusional states. If treated with OZOBAX, these patients should be kept under careful surveillance because exacerbations of these conditions have been observed with oral baclofen administration.
Exacerbation Of Autonomic Dysreflexia
OZOBAX should be used with caution in patients with a history of autonomic dysreflexia. The presence of nociceptive stimuli or abrupt withdrawal of OZOBAX may cause an autonomic dysreflexic episode.
Exacerbation Of Epilepsy
OZOBAX should be used with caution in patients with epilepsy. Deterioration in seizure control has been reported in patients taking baclofen.
Posture And Balance Effects
OZOBAX should be used with caution in patients where spasticity is utilized to sustain upright posture and balance in locomotion or whenever spasticity is utilized to obtain increased function.
Ovarian Cysts
A dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts was observed in female rats treated chronically with oral baclofen. Ovarian cysts have been found by palpation in about 4% of the multiple sclerosis patients who were treated with oral baclofen for up to one year. In most cases, these cysts disappeared spontaneously while patients continued to receive the drug. Ovarian cysts are estimated to occur spontaneously in approximately 1% to 5% of the normal female population.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No increase in tumors was seen in rats receiving baclofen orally for two years at approximately 30 to 60 times on a mg/kg basis, or 10 to 20 times on a mg/ m² basis, the maximum oral dose recommended for human use. Mutagenesis Genetic toxicology assays have not been conducted for baclofen.
Impairment Of Fertility
Studies to evaluate the effects of baclofen on fertility have not been conducted.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of OZOBAX in pregnant women. Oral administration of baclofen to pregnant rats resulted in an increased incidence of fetal structural abnormalities at a dose which was also associated with maternal toxicity. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Ozobax may increase the risk of late-onset neonatal withdrawal symptoms [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Data
Animal Data
Baclofen given orally has been shown to increase the incidence of omphaloceles (ventral hernias) in fetuses of rats given approximately 13 times on a mg/kg basis, or 3 times on a mg/m² basis, the maximum oral dose recommended for human use; this dose also caused reductions in food intake and weight gain in the dams. This abnormality was not seen in mice or rabbits.
Lactation
Risk Summary
At recommended oral doses, baclofen is present in human milk. There are no human data on the effects of baclofen on milk production. There are no adequate data on the effects of baclofen on the breastfed infant. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of OZOBAX is stopped, or when breastfeeding is stopped [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for OZOBAX and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from OZOBAX or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Renal Impairment
Because baclofen is primarily excreted unchanged through the kidneys, OZOBAX should be given with caution to patients with renal impairment, and it may be necessary to reduce the dosage.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Symptoms Of Baclofen Overdose
Patients may present in coma or with progressive drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, accommodation disorders, respiratory depression, seizures, or hypotonia progressing to loss of consciousness.
Treatment For Overdose
The treatment of baclofen overdose includes gastric decontamination, maintaining an adequate airway and respirations.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
OZOBAX is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to baclofen.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
The precise mechanism of action of baclofen is not fully understood. Baclofen inhibits both monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes at the spinal level, possibly by decreasing excitatory neurotransmitter release from afferent terminals, although actions at supraspinal sites may also occur and contribute to its clinical effect. Baclofen is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gammaÂaminobutyric acid (GABA), and may exert its effects by stimulation of the GABAB receptor subtype.
Pharmacodynamics
Baclofen has been shown to have general CNS depressant properties, as indicated by the production of sedation with tolerance, somnolence, ataxia, and respiratory and cardiovascular depression [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, and OVERDOSAGE].
Pharmacokinetics
A pharmacokinetic study in heathy adult male subjects under fasting conditions at 20 mg dose level demonstrated similar bioavailability for baclofen oral solution and oral tablets. The peak plasma concentrations were achieved in about 0.75 hours from oral solution and the apparent elimination half-life is about 5.7 hours. Baclofen is excreted primarily by the kidney in unchanged form, and there is relatively large intersubject variation in absorption and/or elimination.
Clinical Studies
The efficacy of OZOBAX is based upon a bioavailability study in healthy adults comparing baclofen oral tablets to OZOBAX [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients or caregivers to use an oral dosing syringe to correctly measure the prescribed amount of medication. Inform patients that oral dosing syringes may be obtained from their pharmacy.
Risks Related To Sudden Withdrawal Of OZOBAX
Advise patients and caregivers not to discontinue use of OZOBAX without consulting with their healthcare provider because sudden withdrawal of OZOBAX can result in serious complications that include hallucinations, seizures, high fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, multiple organ-system failure, and death [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]. Inform patients that early symptoms of OZOBAX withdrawal may include increased spasticity, itching, and tingling of extremities.
Neonatal Withdrawal Symptoms Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are pregnant,plan to become pregnant, or plan to breastfeed [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and Use In Specific Populations].
Increased Risk Of Drowsiness With Alcohol And Other CNS Depressants
Advise patients that OZOBAX may cause drowsiness, and that they should avoid the operation of automobiles or other dangerous machinery, or activities made hazardous by decreased alertness when starting OZOBAX or increasing the dose until they know how the drug affects them [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]. Inform patients and their caregivers that the drowsiness associated with OZOBAX use can be worsened by alcohol and other CNS depressants. Advise patients to read all medicine labels carefully, and to tell their healthcare provider about all prescription and nonprescription drugs they may use.
Storage
Instruct patients to store OZOBAX in the refrigerator [see HOW SUPPLIED/Storage And Handling].




