Bruises: Causes, Colors, and Treatments
What Is a Bruise?

You bump your leg against the coffee table. You drop something on your toe. You take a spill on the sidewalk while walking the dog. All of these situations may result in a bruise. A bruise happens when small blood vessels underneath the skin become injured and leak blood. This results in a colorful mark under your skin known as a bruise. Bruises may also occur due to certain medical conditions or as a side effect of some medications or treatments. Warfarin is one of several medications associated with excess bruising. It is an anticoagulant medication. Most bruises that are minor injuries heal within approximately 2 weeks. Soft tissues, muscles, and bones may be injured by bruising.
What Causes Bruising?

Injuries bursts tiny blood vessels near the surface of the skin. These blood vessels leak blood into the surrounding area. If the skin is not broken, blood pooled from bleeding under the skin begins to clot. A bruise is the pooled blood that is visible as a colorful mark. More serious injuries cause bigger bruises called contusions. Contusions may be very tender to the touch and cause more pain than less serious bruises.
Are There Different Types of Bruises?

There are several different types of bruises. A bruise that involves bleeding from broken blood vessels leaking into the upper layers of skin is called an ecchymosis. An example of this kind of bruise is a shiner or black eye. Hematomas are bruises that develop when blood clots and forms a lump underneath the surface of the skin. The injured area may be raised, swollen, and painful. A “goose egg” on the forehead is an example of this type of bruise. Children frequently get these types of injuries. The scalp contains a lot of blood vessels so an injury to the head may cause this type of bruise.
What Do the Different Colors of Bruises Mean?

Bruises are usually red or purple discolorations right after an injury. This is because they are the color of the blood that has pooled underneath the skin. As a bruise heals, the body breaks down blood and fluids that have accumulated under the skin. As this happens the bruise turns different colors.
- Within the first few days after getting a bruise, the area may become a black mark, blue mark, or purple mark.
- Within 5 to 10 days after getting a bruise, the area may turn greenish or yellowish.
- During the final phase of healing, approximately 10 to 14 days after getting a bruise, the area will usually be brown in color. As healing progresses, the area will become lighter and lighter until it eventually fades away entirely.
How long do bruises last? Most heal completely within about 2 weeks.
How Do You Treat and Get Rid of Bruises?

When you get a bruise, the area has to proceed through the various healing stages before it fades away completely. There are things you can do to minimize the formation and appearance of a bruise after you receive an injury. You can use first aid on a bruise. Treatment involves placing a cold pack over an area that you’ve bumped or injured to shrink blood vessels and minimize swelling. Cold minimizes fluid leakage into tissues. Do not place a cold pack directly on the skin as it may stick. Wrap a bag of frozen veggies (peas are a good choice) in a towel and place over the injured area. Apply cold for about 15 to 20 minutes. Remove the cold pack for about 30 minutes, then reapply the cold pack to the affected area.
How to Heal a Bruise

If possible, follow the RICE rule (rest area, apply ice bags to area, compress area (reduce swelling and elevate area above the level of the heart). To care for bruises on legs or arms, elevate the limb above the heart to keep blood and fluids from pooling in the injured area. This also helps prevent swelling. Use cold packs for the first 2 days after bruising to shrink blood vessels. After 2 days, use a heating pad or warm compress on the area to ease pain and speed healing. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can decrease pain. Gentle massage can encourage blood flow and encourage healing but not during the first two days as it may cause increased bruising.
What Is a Bone Bruise?

A bruised bone occurs when a traumatic injury results in the accumulation of blood and fluid around a bone. A bone bruise is a less serious injury than a bone fracture, but it is more severe than a regular bruise. Sports injuries and accidents are common causes of bone bruises. Medical conditions like arthritis may cause bone bruises, too. Symptoms of a bone bruise include pain, swelling, and color changes. Bone bruises usually hurt more than regular bruises and they take longer to heal. Tend to a bone bruise by resting, icing and elevating the area, and taking pain relievers. See the doctor if you suffer a severe bruise or a bone bruise.
When Is a Bruise a Sign of Something More Serious?

When is a bruise bad enough to go to the doctor? Minor bruises are not a cause for concern and most heal within 2 weeks. Sometimes, a bruise may be a sign of a more serious condition that needs medical attention. Seek medical care right away if you notice any of the following.
- A bruise that keeps getting bigger after the day of the injury may need medical attention.
- A bruise on a limb that makes your leg or arm feel very tight or swollen requires medical attention.
- If a bruise lasts for longer than 2 weeks or it reappears for an unknown reason, see your doctor.
- Any bruise that occurs around an eye and interferes with vision or makes it difficult to see in different directions is cause for concern.
- Bruises that occur on the trunk, abdomen, or head may be associated with damage to internal organs including the brain. See your doctor if you bruise any of these areas.
- If a bruise is associated with a broken bone or you suspect you may have broken a bone, seek medical attention.
Why Do I Bruise So Much?

Maybe you’re thinking, “Why do I bruise so easily?” Many factors may contribute to you becoming easily bruised. Your gender, age, and genetics may all play a role. Older adults have thinner skin and less fatty tissue under the skin. This fatty tissue protects blood vessels. Without it, blood vessels under the skin may be injured more easily. Women bruise more readily than men, especially from slight bumps and injuries to the thighs, upper arms, and buttocks. Women have thinner skin and more subcutaneous fat than men. That’s why they bruise more easily. Conditions that affect blood clotting or connective tissue may predispose people in some families to bruise easily. Taking certain medications may make you bruise more easily, too.
Other Spots That Look Like Bruises
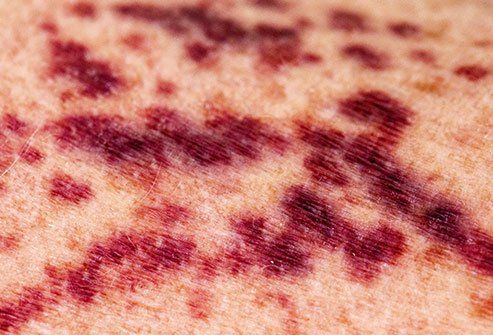
Some conditions are associated with marks that resemble bruises but are not bruises. Large reddish or purple spots that appear under the skin are called purpura. Smaller spots are called petechiae. Conditions that may cause these skin discolorations include inadequate platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia), certain cancers (Hodgkin’s disease, multiple myeloma, leukemia), liver disease (cirrhosis), or bleeding disorders (von Willebrand’s disease, hemophilia). See your doctor if you suffer from unexplained bruises or marks on your skin.
Nutrients and Bruising

Certain nutrients are necessary to maintain proper blood clotting and healthy skin and blood vessels. These nutrients include folate and vitamins C, B12, and K. Without sufficient levels of these nutrients, you may bruise more easily. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruit, cantaloupe, mango, and berries. Increase your levels of B12 by eating more fortified cereal and beef. Leafy green veggies are great sources of folate and vitamin K.
Do Medications Cause Bruises?

Certain medications affect blood clotting and may make you bruise more easily. Corticosteroids, blood thinners, chemotherapy, and aspirin are just some medications that increase the risk of bruises. Never stop taking a medication or change the dose of a medication without talking to your doctor. If you think one or more of your medications is contributing to easy bruising, have a conversation with your doctor. He or she may be able to switch you to another medication that does not have that side effect.
Can Bruises Be Prevented?

It is not possible to avoid bruises completely, but there are things you can do to minimize the risk that you’ll get hurt. Prevent falls in the home by removing throw rugs from walking paths throughout the house. Move furniture to areas where you won’t bump into or trip over pieces. Install nightlights so you have adequate illumination when you’re walking around at night. If you play sports, wear protective gear to protect your head, shins, knees, and elbows from crashes and falls.
Bruises: Causes, Colors, and Treatments
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
- iStock
- Medical Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
- Getty Images
REFERENCES:
- American Family Physician: “Bleeding and Bruising: A Diagnostic Work-up.”
- BMJ: “Purpuric and Petechial Rashes in Adults and Children: Initial Assessment.”
- Musculoskeletal Diseases 2009-2012: Diagnostic Imaging: “Trauma Related BME.”
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases: “Questions and Answers about Sprains and Strains.”
- National Council on Aging: “Falls Prevention.”
- The Nemours Foundation: “Bruises,” "Head injuries."
- Nutrients in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease: “Physical and Clinical Assessment of Nutrition Status.”
- Textbook of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology: “Chapter 14: Injuries by Blunt Force.”
© 1996-2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on OnHealth
